Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Scalar field sensors in 3D¶
This example demonstrates the application of the pyvale sensor simulation module to scalar fields in 3 spatial dimensions. An example of a scalar field sensor would be a thermocouple or resistance temperature detector measuring a temperature field.
Note that this example has minimal explanation and assumes you have reviewed the basic sensor simulation examples to understand how the underlying engine works as well as the sensor simulation workflow.
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# pyvale imports
import pyvale.mooseherder as mh
import pyvale.sensorsim as sens
import pyvale.dataset as dataset
1. Load physics simulation data¶
data_path = dataset.thermal_3d_path()
sim_data = mh.ExodusLoader(data_path).load_all_sim_data()
sim_data = sens.scale_length_units(scale=1000.0,
sim_data=sim_data,
disp_keys=None)
2. Build virtual sensor array¶
sim_dims = sens.simtools.get_sim_dims(sim_data)
sens_pos: np.ndarray = sens.gen_pos_grid_inside(num_sensors=(1,4,1),
x_lims=(12.5,12.5),
y_lims=sim_dims["y"],
z_lims=sim_dims["z"])
sample_times = np.linspace(0.0,np.max(sim_data.time),50)
sens_data = sens.SensorData(positions=sens_pos,
sample_times=sample_times)
descriptor = sens.SensorDescriptor(name="Temperature",
symbol="T",
units = r"^{\circ}C",
tag = "TC")
sens_array: sens.SensorsPoint = sens.SensorFactory.scalar_point(
sim_data,
sens_data,
comp_key="temperature",
spatial_dims=sens.EDim.THREED,
descriptor=descriptor,
)
2.1. Add simulated measurement errors¶
error_chain: list[sens.IErrSimulator] = [
sens.ErrSysOffset(offset=-10.0),
sens.ErrSysGen(sens.GenUniform(low=-5.0,high=5.0)),
sens.ErrRandGen(sens.GenNormal(std=5.0)),
sens.ErrRandGenPercent(sens.GenUniform(low=-2.0,high=2.0)),
]
sens_array.set_error_chain(error_chain)
3. Create & run simulated experiment¶
measurements: np.ndarray = sens_array.sim_measurements()
truth: np.ndarray = sens_array.get_truth()
sys_errs: np.ndarray = sens_array.get_errors_systematic()
rand_errs: np.ndarray = sens_array.get_errors_random()
print(80*"-")
print("measurement = truth + sysematic error + random error")
print(f"measurements.shape = {measurements.shape} = "
+ "(n_sensors,n_field_components,n_timesteps)")
print(f"truth.shape = {truth.shape}")
print(f"sys_errs.shape = {sys_errs.shape}")
print(f"rand_errs.shape = {rand_errs.shape}")
sens_print: int = 0
comp_print: int = 0
time_last: int = 5
time_print = slice(measurements.shape[2]-time_last,measurements.shape[2])
print(f"\nThese are the last {time_last} virtual measurements of sensor "
+ f"{sens_print}:\n")
sens.print_measurements(sens_array,sens_print,comp_print,time_print)
print("\n"+80*"-")
4. Analyse & visualise the results¶
output_path = Path.cwd() / "pyvale-output"
if not output_path.is_dir():
output_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
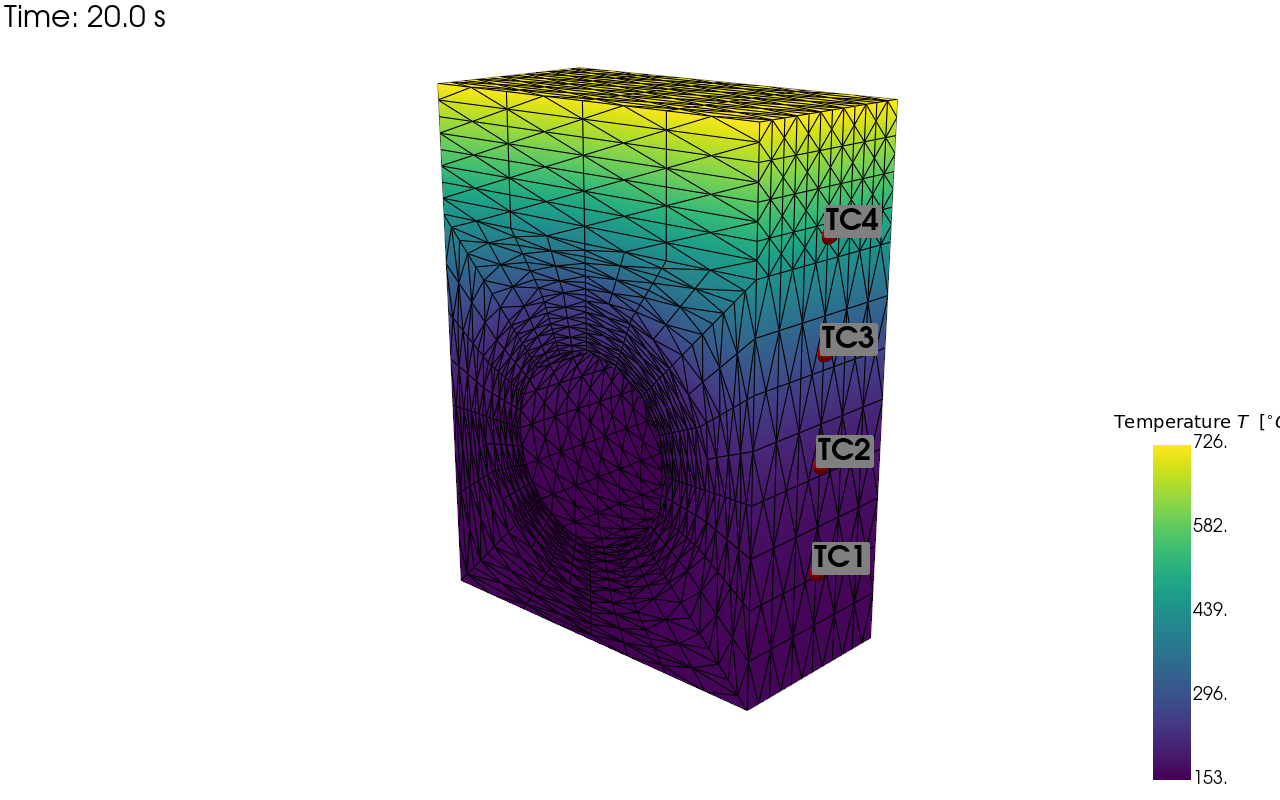
pv_plot = sens.plot_point_sensors_on_sim(sens_array,
comp_key="temperature")
pv_plot.camera_position = [(59.354, 43.428, 69.946),
(-2.858, 13.189, 4.523),
(-0.215, 0.948, -0.233)]
# Set to False to show an interactive plot instead of saving the figure
pv_plot.off_screen = True
if pv_plot.off_screen:
pv_plot.screenshot(output_path/"ext_ex3b_locs.png")
else:
pv_plot.show()
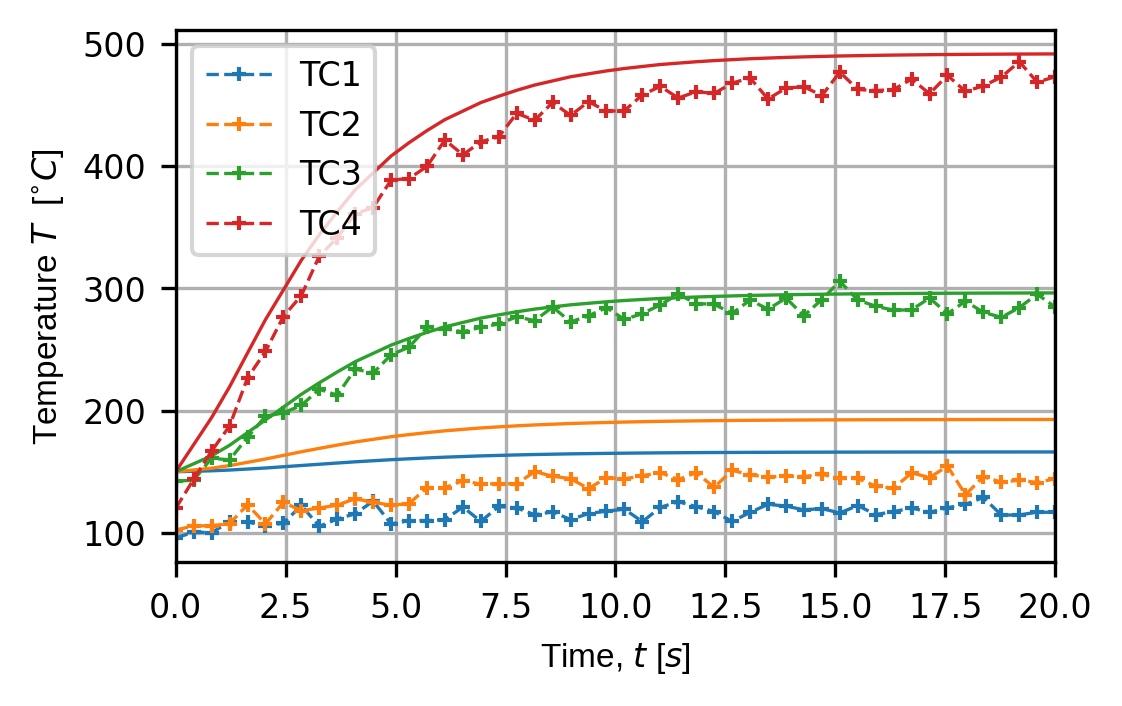
(fig,ax) = sens.plot_time_traces(sens_array,comp_key="temperature")
fig.savefig(output_path/"ext_ex3b_traces.png",dpi=300,bbox_inches="tight")
# Uncomment this to display the sensor trace plot
# plt.show()